Integration¶
The Gini Bank SDK has two main features: capturing invoices for information extraction and handling payment requests. Both can be used independently and you may opt to use only one or both in your app.
Capturing Invoices¶
The capture feature uses our Gini Capture SDK to provide Activities and Fragments to capture invoices and prepare them for upload to the Gini Bank API. It also allows documents to be imported from other apps. The captured images can be reviewed and are optimized on the device to provide the best results when used with the Gini Bank API.
Android Manifest¶
The capture feature of the SDK uses the camera therefore the camera permission is required:
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="...">
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CAMERA" />
</manifest>
Note
Make sure you request the camera permission before starting the SDK.
Requirements Check¶
We recommend running our runtime requirements check first before launching the Gini Capture SDK to ensure the device is capable of taking pictures of adequate quality.
Simply run GiniBank.checkCaptureRequirements() and inspect the returned RequirementsReport for the result:
Note
On Android 6.0 and later the camera permission is required before checking the requirements.
final RequirementsReport report = GiniBank.checkCaptureRequirements((Context) this);
if (!report.isFulfilled()) {
final StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
report.getRequirementReports().forEach(requirementReport -> {
if (!requirementReport.isFulfilled()) {
stringBuilder.append(requirementReport.getRequirementId());
stringBuilder.append(": ");
stringBuilder.append(requirementReport.getDetails());
stringBuilder.append("\n");
}
});
Toast.makeText(this, "Requirements not fulfilled:\n" + stringBuilder,
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
Configuration¶
Configuration and interaction is done using CaptureConfiguration. To set the configuration use the
GiniBank.setCaptureConfiguration() static method.
Important
The configuration is immutable and make sure to call GiniBank.releaseCapture() before setting a new
configuration.
You should call GiniBank.releaseCapture() after the SDK returned control to your application and your app has
sent feedback to the Gini Bank API and is not using the capture feature anymore.
To view all the configuration options see the documentation of CaptureConfiguration.
Information about the configurable features are available on the Capture Features page.
Tablet Support¶
The Gini Bank SDK can be used on tablets, too. Some UI elements adapt to the larger screen to offer the best user experience for tablet users.
Many tablets with at least 8MP cameras don’t have an LED flash. Therefore we don’t require flash for tablets. For this reason the extraction quality on those tablets might be lower compared to smartphones.
On tablets landscape orientation is also supported (smartphones are portrait only). We advise you to test your integration on tablets in both orientations.
In landscape the camera screen’s UI displays the camera trigger button on the right side of the screen. Users can reach the camera trigger more easily this way. The camera preview along with the document corner guides are shown in landscape to match the device’s orientation.
Other UI elements on all the screens maintain their relative position and the screen layouts are scaled automatically to fit the current orientation.
Networking¶
The Gini Bank SDK allows you to use the default networking implementation of our Gini Capture SDK to communicate with the Gini Bank API. You may also implement your own networking layer.
Note
You should have received Gini Bank API client credentials from us. Please get in touch with us in case you don’t have them. Without credentials you won’t be able to use the Gini Bank API.
Default Implementation¶
The capture feature is not aware of any networking implementations and requires you to set them in the
CaptureConfiguration.
The default networking implementations are the GiniCaptureDefaultNetworkService and
GiniCaptureDefaultNetworkApi. We provide you with two helper methods to create them with the minimal configuration:
val networkService = getDefaultNetworkService(
context = this,
clientId = myClientId,
clientSecret = myClientSecret,
emailDomain = myEmailDomain,
documentMetadata = myDocumentMetadata
)
val networkApi = getDefaultNetworkApi(networkService)
GiniBank.setCaptureConfiguration(
CaptureConfiguration(
networkService = networkService,
networkApi = networkApi
)
)
For all configuration options of the default networking implementation see the documentation of GiniCaptureDefaultNetworkService.Builder and GiniCaptureDefaultNetworkApi.Builder.
Retrieve the Analyzed Document¶
You can call GiniCaptureDefaultNetworkService.getAnalyzedGiniApiDocument() after the Gini Bank SDK has returned
extractions to your application. It returns the Gini Bank API document which was created when the user uploaded an
image or pdf for analysis.
When extractions were retrieved without using the Gini Bank API, then it will return null. For example when the
extractions came from an EPS QR Code.
Note
Make sure to call it before calling GiniCaptureDefaultNetworkService.cleanup() or GiniBank.releaseCapture().
Otherwise the analyzed document won’t be available anymore.
Custom Implementation¶
You can also provide your own networking by implementing the GiniCaptureNetworkService and the
GiniCaptureNetworkApi interfaces:
GiniCaptureNetworkService- This interface is used to upload, analyze and delete documents. See the reference documentation for details.
GiniCaptureNetworkApi- This interface is used to declare network tasks which should be called by you outside of the Gini Capture SDK (e.g., for sending feedback after the user saw and potentielly corrected the extractions). See the reference documentation for details.
You may also use the Gini Bank API Library for Android or implement communication with the Gini Bank API yourself.
Sending Feedback¶
Your app should send feedback for the extractions the Gini Bank API delivered. Feedback should be sent only for the extractions the user has seen and accepted (or corrected).
For addition information about feedback see the Gini Bank API documentation.
Default Implementation¶
The example below shows how to correct extractions and send feedback using the default networking implementation:
Note
We also provide a sample test case here to verify that extraction feedback sending works. You may use it along with the example pdf and json files as a starting point to write your own test case.
The sample test case is based on the Bank API documentation’s recommended steps for testing extraction feedback sending.
val networkApi: GiniCaptureDefaultNetworkApi // Provided
val extractions: Map<String, GiniCaptureSpecificExtraction> // Provided
// Modify the amount to pay extraction's value.
GiniCaptureSpecificExtraction amountToPay = extractions["amountToPay"];
amountToPay.value = "31.00:EUR"
// You should send feedback only for extractions the user has seen and accepted.
// In this example only the amountToPay was wrong and we can reuse the other extractions.
val feedback = mapOf<String, GiniCaptureSpecificExtraction>(
"iban" to mExtractions["iban"],
"amountToPay" to amountTopay,
"bic" to mExtractions["bic"],
"senderName" to mExtractions["sencerName"]
)
networkApi.sendFeedback(feedback, object : GiniCaptureNetworkCallback<Void, Error> {
override fun failure(error: Error) {
// Handle the error.
}
override fun success(result: Void?) {
// Feedback sent successfully.
}
override fun cancelled() {
// Handle cancellation.
}
})
Custom Implementation¶
If you use your own networking implementation and directly communicate with the Gini Bank API then see this section in its documentation on how to send feedback.
In case you use the Gini Bank API Library then see this section in its documentation for details.
Note
The Bank API documentation provides recommended steps for testing extraction feedback sending. You may use it along with the example pdf and json files as a starting point to write a test case for verifying that feedback sending works.
Capture Flow¶
The capture flow can be used in two ways, either by using the Screen API or the Component API:
- The Screen API provides activities for easy integration that can be customized in a limited way. The screen and configuration design is based on our long-lasting experience with integration in customer apps.
- In the Component API we provide fragments for advanced integration with more freedom for customization.
Screen API¶
This is the easiest way to use the capture flow. You only need to:
- Request camera access,
- Configure the capture feature using the
CaptureConfiguration, - Register an activity result handler with the
CaptureFlowContract(), - Start the capture flow.
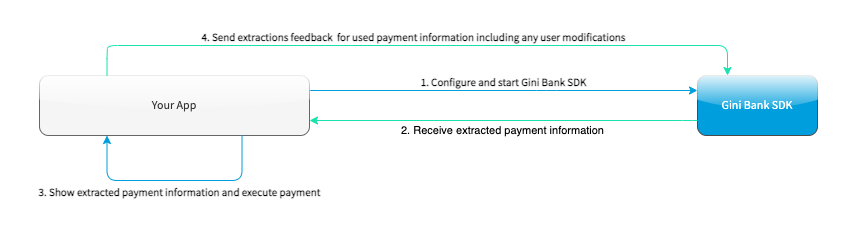
The following diagram shows the interaction between your app and the SDK:
Note
Check out the Screen API example app to see how an integration could look like.
The following example shows how to launch the capture flow using the Screen API and how to handle the results:
// Use the androidx's Activity Result API to register a handler for the capture result.
val captureLauncher = registerForActivityResult(CaptureFlowContract()) { result: CaptureResult ->
when (result) {
is CaptureResult.Success -> {
handleExtractions(result.specificExtractions)
}
is CaptureResult.Error -> {
when (result.value) {
is ResultError.Capture -> {
val captureError: GiniCaptureError = (result.value as ResultError.Capture).giniCaptureError
handleCaptureError(captureError)
}
is ResultError.FileImport -> {
// See the File Import section on the Capture Features page for more details.
val fileImportError = result.value as ResultError.FileImport
handleFileImportError(fileImportError)
}
}
}
CaptureResult.Empty -> {
handleNoExtractions()
}
CaptureResult.Cancel -> {
handleCancellation()
}
}
}
fun launchGiniCapture() {
// Make sure camera permission has been already granted at this point.
// Check that the device fulfills the requirements.
val report = GiniCaptureRequirements.checkRequirements((Context) this)
if (!report.isFulfilled()) {
handleUnfulfilledRequirements(report)
return
}
// Instantiate the networking implementations.
val networkService: GiniCaptureNetworkService = ...
val networkApi: GiniCaptureNetworkApi = ...
// Cleanup to make sure everything is reset.
GiniBank.releaseCapture(this)
// Configure the capture feature.
GiniBank.setCaptureConfiguration(
CaptureConfiguration(
networkService = networkService,
networkApi = networkApi,
...
)
)
// Launch and wait for the result.
GiniBank.startCaptureFlow(captureLauncher)
}
Component API¶
This is the more complicated way of using the capture flow. The advantage is that it is based on fragments and you have full control over how these are shown in your UI.
Note
Check out the Component API example app to see how an integration could look like.
Before launching the first fragment you need to:
- Request camera access,
- Configure the capture feature using the
CaptureConfiguration.
The Component API is exposed as-is from the Gini Capture SDK and you can follow it’s guide to learn how to integrate it.
Handling Payment Requests¶
The Gini Bank SDK enables your app to handle payment requests started by other Gini SDKs (e.g., Gini Health SDK) in another app. You can retrieve the payment requests’s content, mark the payment request as payed and also return your user to the app that created the payment request.
Networking¶
The pay feature depends on the Gini Bank API Library, which
provides an entry point through the GiniBankAPI class.
Note
You should have received Gini Bank API client credentials from us. Please get in touch with us in case you don’t have them. Without credentials you won’t be able to use the Gini Bank API.
The GiniBankAPI class can be built either with client credentials or with a SessionManager if you already have an
authorization token. We provide helper methods for each case:
getGiniApi(context: Context, clientId: String, clientSecret: String,
emailDomain: String)
getGiniApi(context: Context, sessionManager: SessionManager)
SessionManager is an interface which you need to implement to send the token.
For more details about the GiniBankAPI class see the Gini Bank API Library’s documentation.
Once you have a GiniBankAPI instance you need to pass it to GiniBank.setGiniApi():
val giniApi = getGiniApi(this, myClientId, myClientSecret, myEmailDomain)
GiniBank.setGiniApi(giniApi)
Android Manifest¶
To be able to receive payment requests you need to add an intent filter for the ginipay URI to your manifest. This also allows other Gini SDKs (e.g., Gini Health SDK) to detect if your app is installed:
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<data
android:host="payment"
android:scheme="ginipay" />
</intent-filter>
The intent filter can be added to the activity which will handle the payment flow of that payment request.
Package Name¶
You also need to tell us your app’s package name. It will be associated with the payment provider we create for your banking app in the Gini Bank API. Other Gini SDKs (like the Gini Health SDK) will only open your banking app if it is installed and it has the same package name as the one known by the Gini Bank API.
If you have different package names for development and production then please share both of them with us so that we can use the right one for each environment.
Receive Payment Requests¶
Note
You can see an example implementation in the Screen API example app’s pay package.
When your activity is launched with an intent you should follow the steps below to receive and handle the payment request:
Extract the payment request id from the intent with
getRequestId():val requestId = getRequestId(intent)
Retrieve the payment details set by other Gini SDKs (like the Gini Health SDK) using
GiniBank.getPaymentRequest():val paymentRequest: PaymentRequest = giniBank.getPaymentRequest(requestId)
Show the payment details to your user:
showPaymentDetails( paymentRequest.recipient, paymentRequest.iban, paymentRequest.bic, paymentRequest.amount, paymentRequest.purpose )
After your user has initiated the payment mark the payment request as paid using
GiniBank.resolvePaymentRequest():// The actual payment details used for the payment (as corrected and accepted by the user). val usedPaymentDetails = ResolvePaymentInput( recipient = "...", iban = "...", bic = "...", amount = "...", purpose = "..." ) val resolvedPayment: ResolvedPayment = giniBank.resolvePaymentRequest(requestId, usedPaymentDetails)
You can allow your user to return to the app that started the flow using
GiniBank.returnToPaymentInitiatorApp():giniBank.returnToPaymentInitiatorApp(context, resolvedPayment)
Testing¶
Testing the payment feature requires an app which uses a Gini SDK which can create payment requests. The Gini Health SDK is one such SDK. You can use it to create payment requests and to forward them to your banking app to view and resolve those payment requests.
Requirements¶
Example app for creating payment requests¶
An example app is available in the Gini Health SDK’s repository.
You can use the same Gini Bank API client credentials in that example app as in your app, if not otherwise specified.
Development Gini Bank API client credentials¶
In order to test using the example app you need to use development client credentials. This will make sure the example will use a payment provider which will open your development banking app.
End to end testing¶
After you’ve set the client credentials in the Gini Health SDK’s example app you can install it along with your banking app on your device.
Run the example app and import an invoice or take a picture of one to start the payment flow.
After following the integration steps above your banking app will be launched and you’ll be able to fetch the payment request, show the payment information and resolve the payment after the transaction has been confirmed. At this point, you may redirect back to the example app.
With these steps completed you have verified that your app, the Gini Bank API, the Gini Health SDK and the Gini Bank SDK work together correctly.
Testing in production¶
The steps are the same but instead of the development client credentials you will need to use production client credentials. This will make sure the Gini Health SDK receives real payment providers including the one which opens your production banking app.
For testing the flow using the example app please make sure that the production client credentials are used before installing it.
You can also test with a real app which uses the Gini Health SDK (or another similar Gini SDK). Please contact us in case you don’t know which app(s) to install for starting the payment flow.